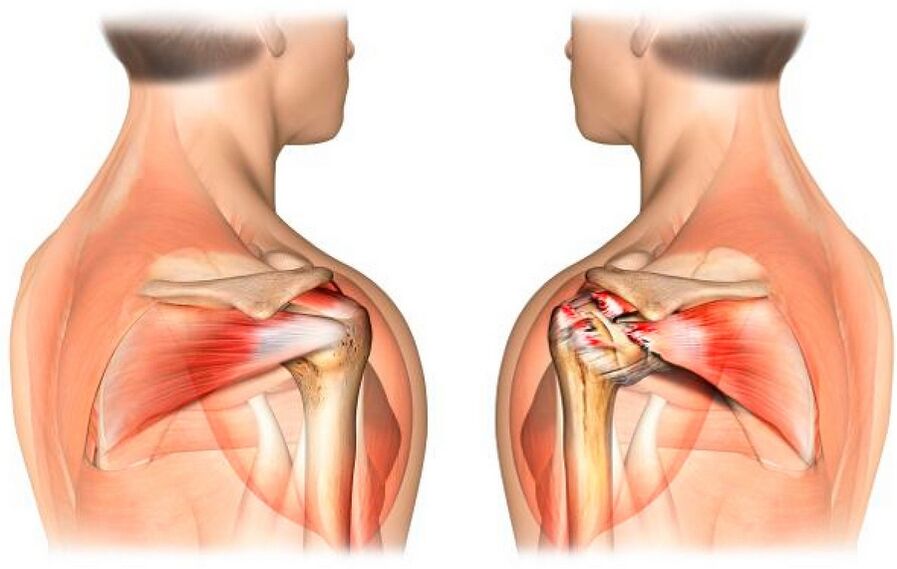
Deforming osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint is a common pathology, especially in elderly patients. The disease is chronic and rapidly developing. It is equally often diagnosed in patients of both sexes. Due to degenerative diseases, damage is observed not only in the cartilaginous tissue of the joint, but also in the bone tissue. The causes of the problem are microtraumatic injuries to the shoulder joint and inflammatory processes developing in it. The cartilaginous tissue gradually becomes thinner, microcracks appear, in which salt deposits accumulate. Then, destructive processes gradually affect the bones, which become denser, grow and, ultimately, change their anatomical shape. The disease progresses over a long period of time without causing any discomfort to the individual in the initial stages of the disease. In fact, this is where the danger lies. Let us look in more detail at the causes, symptoms, as well as how and with what to treat deforming osteoarthritis.
Why does the pathology occur?
Among the causes of arthrosis of the shoulder joint, experts name the following conditions and factors.
Traumatic injuries
Shoulder injuries include intra-articular fractures, dislocations, and bruises. Fractures are characterized by the fact that the fracture line is located in the joint cavity. In addition to bone, it also affects cartilage, causing additional injuries: ligaments are torn, the capsule is damaged.
Shoulder dislocation is one of the most common injuries, often leading to complications, joint deformation and the development of osteoarthritis. As a result, the joint may completely lose mobility.
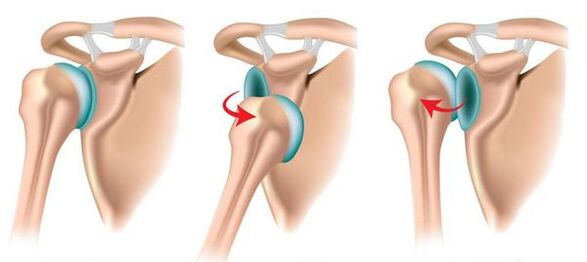
Right shoulder dislocations are seen more frequently in right-handers and left shoulder dislocations in left-handers.
Bruises occur as a result of a strong blow, for example due to an accident, fall or playing sports. Due to a bruise, the bones do not shift, the cartilaginous tissue is not destroyed, but their normal nutrition is disturbed, which can also lead to post-traumatic arthrosis.
Increased load
Excessive load on the shoulder joint is observed in some groups of people:
- Professional athletes: volleyball players, tennis players, track and field athletes.
- Builders, plasterers, loaders.
- Summer resident.
Everyone has to do the same type of movements with their hand raised for a long time. Therefore, they have microcracks and injuries, sprained ligaments, overstrained muscles, and the functioning of blood vessels is disrupted. The joint lacks nutrients and becomes deformed.
If a person does not monitor the load and does not take preventive measures, glenohumeral osteoarthritis may develop.
Joint pathologies
Some joint pathologies can cause the development of deforming osteoarthritis.
- Synovitis. Its cause is an infection that causes intense formation of intra-articular fluid. Due to the accumulation of fluid, the joint swells and begins to hurt. Most often, this problem is observed in connection with a shoulder injury. If synovitis is not treated, there is a high probability of complications. The disease is treated with therapeutic agents. Pain is relieved by NSAIDs. In addition, the patient will undergo a puncture to pump out the fluid accumulated inside the joint. The shoulder is then fixed in a stationary position. Synovitis of an infectious nature is treated with antibiotics. In the most difficult situations, surgical treatment is performed.
- Arthritis of the shoulder joint of various origins. Its signs: shoulder swelling and severe joint pain.
- Bone necrosis also causes osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint. Triggered by injury or genetics, it is characterized by the fact that bone cells begin to die. Medicine offers therapeutic or surgical correction of the condition, depending on the stage of the disease and the individual characteristics of the organism. Chondroprotectors restore bone tissue, and NSAIDs help to cope with pain. The use of medications is complemented by physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy.
Heredity, congenital and acquired pathologies
Various anomalies in the structure of the shoulder (congenital or acquired) almost always deform it. The consequence of muscular dystrophy is insufficient nutrition of the joint tissues and then arthrosis of the shoulder.
If a person has a lack of collagen, this will also provoke the development of pathology.
The likelihood of developing shoulder arthrosis is much higher in those people whose relatives had similar problems, including coxarthrosis, gonarthrosis, becauseunderdevelopment of cartilaginous tissue is inherited.
Blood vessel diseases
The condition under which the likelihood of arthrosis of the shoulder joint increases is considered to be various disorders in the functioning of blood vessels.
- Physical inactivity also significantly increases the possibility of developing pathology. It is caused by insufficient physical activity. The disease is characterized by apathy, drowsiness, decreased appetite and insomnia. One of the most common complications of physical inactivity is cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis. The disease is treated conservatively, diet and exercise therapy are also required.
- Endarteritis obliterans. Pathology occurs due to impaired blood circulation, which results in a lack of oxygen supply to the vessel tissues. So their performance is limited and then they die.
- Poor nutrition and insufficient physical activity are conditions for obesity and metabolic disorders, which hinder blood circulation in joint tissues. The result of the process is the development of osteoarthritis.
- Varicose veins, in which blood flow in the vessels slows down, are also one of the conditions that cause degenerative changes in the joints.
Hormonal imbalances and weakened immunity
Disturbed hormonal levels and reduced immunity can become a factor causing destructive tendencies in joint tissues.
- The changes that occur in a woman's body due to menopause are characterized by metabolic disorders. The lack of calcium in the bones during this period is the result of a decrease in estrogen levels in the female body. The consequence of these processes is possible arthrosis of the joints.
- Psoriasis is a chronic non-infectious pathology caused by various reasons (stress, decreased immunity, impaired metabolism, etc. ). The disease is systemic, therefore, under certain conditions, not only the skin, but also internal organs, bones and joints can be affected.
- Men often suffer from osteoarthritis due to gout. It occurs due to excessive accumulation of uric acid in the form of small crystals in the joints. Signs of pathology include joint swelling and pain. Externally, its manifestation can be noticed at the time of paroxysmal exacerbation of gout. Most often this happens at night. The shoulder feels hot and the skin turns red. In an advanced situation, gout can become a provoking factor in the development of the pathology. To avoid complications, gout must be treated with medications, not forgetting about diet and exercise therapy.
- Reduced immunity can be the cause of arthrosis due to the exacerbation of inflammatory processes in the joint cavities.
Impaired metabolism
Lack of intake of various vitamins and microelements in the body (especially calcium, phosphorus, vitamin D) often causes a lack of nutrition of the intra-articular fluid, cartilage and bone tissue of the joint, which in turn causes degeneration- changes dystrophic in them.
Due to diabetes, blood vessels become thinner, blood flow through them decreases, and periarticular tissues do not receive enough nutrients. All this leads to osteoarthritis.
Age-related changes
With age, bones and cartilage tissue become thinner and weaker. The likelihood of developing shoulder osteoarthritis after age 50 increases markedly.

Most often, shoulder arthrosis is observed due to exposure to a complex of the listed conditions.
Symptoms
Deforming osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint is characterized as a disease that develops gradually over a long period of time. Initially it presents practically nothing, however, in later stages of development the following symptoms are observed.
- Pain in the shoulder. Its character, most often painful, pulling, bothers the person in the morning, after a night's rest. It may occur before a climate change. If physical activity is required on the affected shoulder, the pain becomes intense and pronounced. As the situation worsens, the pain syndrome manifests itself even at rest. Using an orthosis helps solve the problem.
- Impaired motor activity of the affected arm occurs due to severe pain. Exacerbation often occurs due to hypothermia or sprained ligaments. The patient is unable to lift their arm or perform normal movements. He feels unbearable pain when performing circular movements on his shoulder or when trying to move his arm behind his back. If therapy is not started in a timely manner, complete immobilization of the upper limbs may occur.
- Clicks and creaks in the joint are initially not very noticeable and can be almost imperceptible. They later become intense and can be heard not only by the patient, but also by the people around them.
- Inflammation in the joint is manifested by edema, swelling, local increase in skin temperature and redness.
- The feeling of stiffness in the joint is caused by growths of bone tissue - osteophytes, which appear if the disease is advanced.
Development of the disease
The disease goes through three phases in its development. Symptoms at each stage are similar to each other, but differ markedly in intensity.
1st degree osteoarthritis
1st degree arthrosis of the shoulder joint is characterized by mild pain in the morning and evening. The patient "develops" the joint with effort before performing the movements. A mild shoulder crunch is possible if a person shakes their hand forcefully. At rest, no pain is felt.
High school
Arthrosis of the shoulder joint of the 2nd degree is manifested by more intense pain, a crunching sound in the shoulder is clearly audible. The mobility of the hand is still preserved, but is already visibly reduced. The destructive process is already present, the joint tissues gradually become thinner and dystrophy is observed. Ligaments, cartilage and bones are affected. Wearing a special orthopedic device - a brace or bandage - helps reduce the intensity of pain.
Arthrosis 3 degrees
The third degree of the disease is the most serious. The symptoms of osteoarthritis significantly alter a person's quality of life. The patient can only slightly rotate his arm, constantly feels sharp pain in the shoulder and deformation of the joint is observed. Muscles partially atrophy. The problem is resolved with surgery. In its absence, complete immobility and disability are likely.
Treatment
It is completely impossible to cure deforming osteoarthritis. You can only slow down its progression and influence the symptoms. Doctors offer two types of treatment for deforming osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint: therapeutic and surgical.
Therapeutic treatment
As a therapeutic correction of the patient's condition, doctors suggest using the following groups of medications.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The main goal at this stage of treatment is to relieve inflammation and pain. Medicines suppress inflammatory processes and relieve pain. It is important to remember that NSAIDs are used for a limited time. They are prescribed in the form of tablets and injections.
- Treatment of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint involves the use of corticosteroids. They help relieve inflammation, thereby stopping the development of pathology.
- Chondroprotectors for arthrosis are prescribed in the non-acute phase to restore damaged cartilage and bone tissue. These medicines are based on several active substances: glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid. They help prevent the destruction of cartilaginous tissue and restore it. But the effectiveness of using chondroprotectors can only be expected in the initial stages of the disease, sinceFor their action the main condition is necessary - cartilaginous tissue must remain in the affected joint. Otherwise, these medicines will not help. All of these medications are prescribed by a doctor. You can expect positive results from its use no earlier than six months of use.
- External agents (ointments, gels, creams) are also widely used in the treatment of osteoarthritis.
- Painkillers also relieve pain and are used inconsistently.
Surgery
The operation is performed at the third degree of development of pathology. It consists of prosthetic replacement of the shoulder and scapula. Surgical treatment has contraindications, most often due to the patient's advanced age.
The decision on how to treat arthrosis of the shoulder joint will be made by the orthopedist or traumatologist.
Additional methods of conservative treatment of shoulder osteoarthritis include exercise therapy, massage and traditional medicine. A prerequisite for these methods is that they cannot be used during a period of exacerbation.
With shoulder arthrosis, physiotherapy can significantly alleviate the patient's condition. In the set of exercises, it is necessary to select simple movements (circular movements, lifting, flexion-extension of the arm). Gymnastics is performed at a calm pace, without overload.
Self-treatment
For home treatment, you can use folk recipes. But its use must be agreed with the attending physician.
- Rubbing the painful joint helps a lot in treating osteoarthritis. The mixture is prepared with 50 g of elecampane root and 125 ml of vodka. The tincture is left for two weeks in a dark place and then used to rub the shoulder before bed.
- Oatmeal compresses are easy to make yourself. Take 30 g of flakes per half liter of water and boil for 8-10 minutes. The decoction is moistened with gauze folded several times and then applied to the affected joint for half an hour.
- You can use cabbage leaves as a compress (at night). They handle pain well.
- Herbal baths are recommended for the treatment of deforming osteoarthritis. Mustard, mint and burdock are used to prepare them.

Osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint, like any other joint disease, cannot be ignored. Your treatment must be approached comprehensively, follow the doctor's instructions: take medications in a disciplined manner, perform a set of therapeutic exercises. To prevent osteoarthritis, you should not strain your joints too much, avoid excessive cooling and watch your diet.

















































